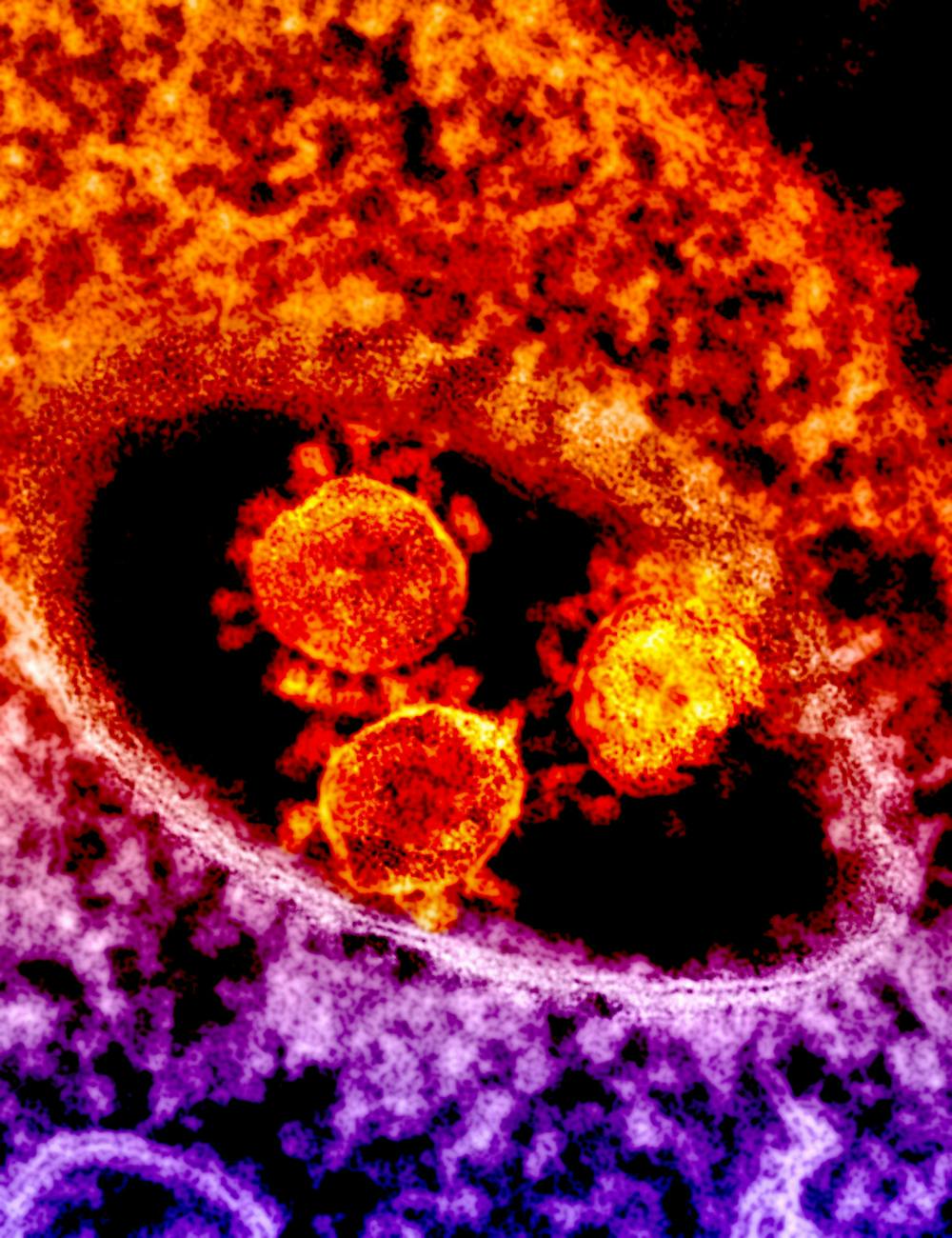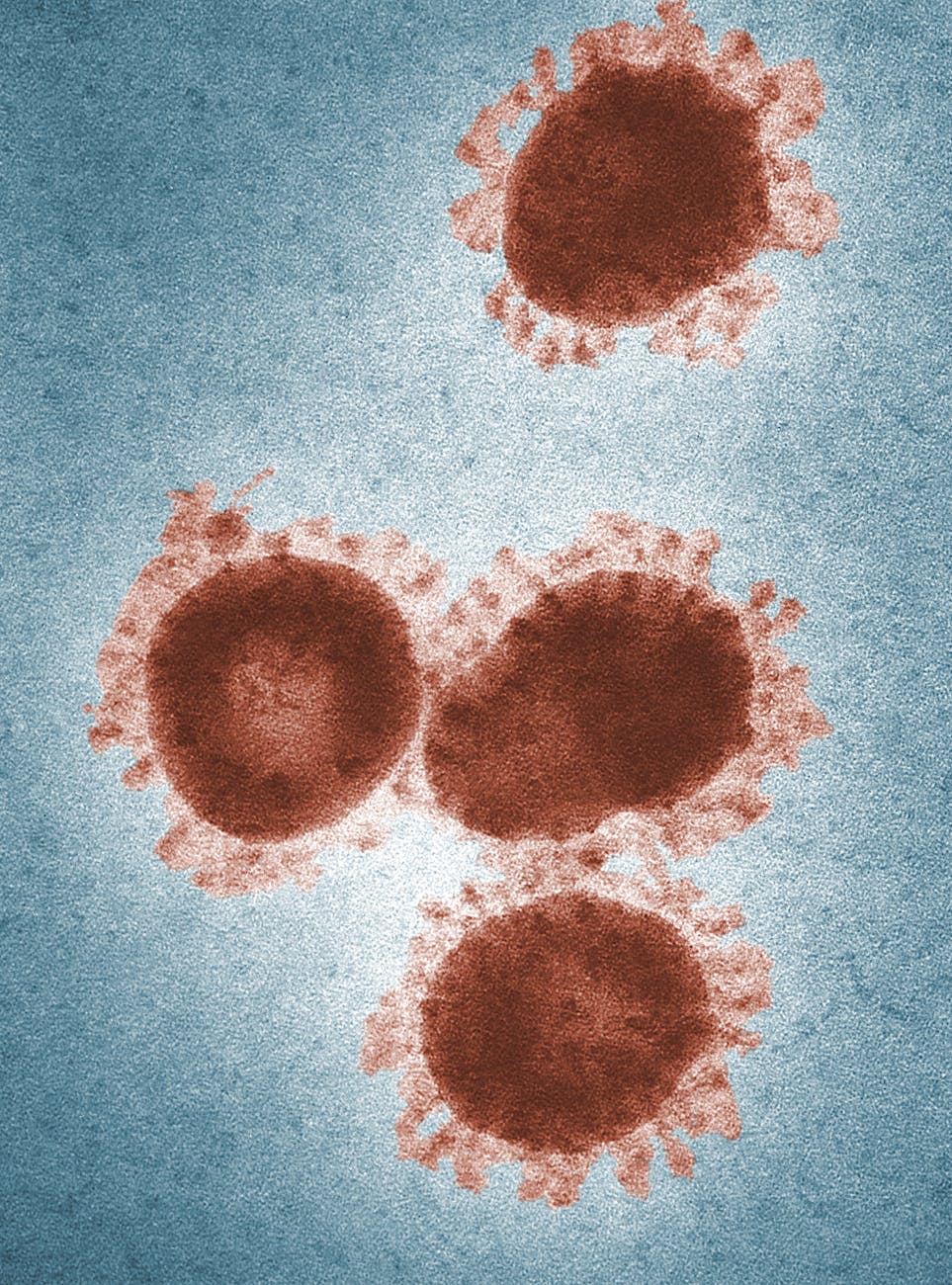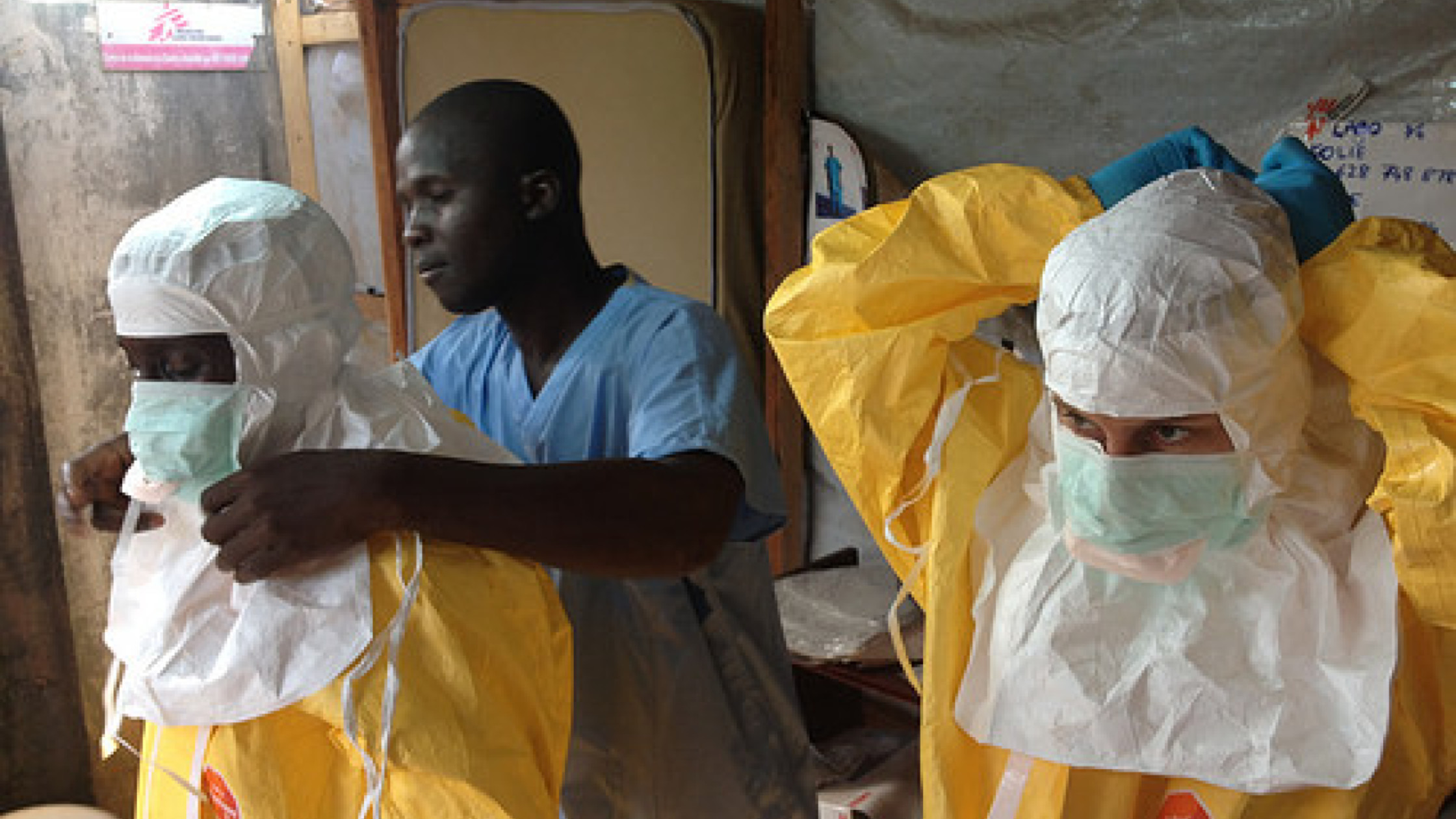
Marburg Virus is a rare but highly dangerous disease caused by a virus from the same family as Ebola. It can cause severe illness in humans, with a high risk of death if not treated promptly. The virus is named after the city of Marburg in Germany, where it was first identified in 1967.
Causes
Marburg Virus is transmitted to humans from fruit bats, which are its natural hosts. The virus can spread through direct contact with the blood, body fluids, or tissues of infected people or animals. It can also spread indirectly through surfaces contaminated with these fluids. Human-to-human transmission usually occurs in families, healthcare settings, or during burial rituals.
Symptoms
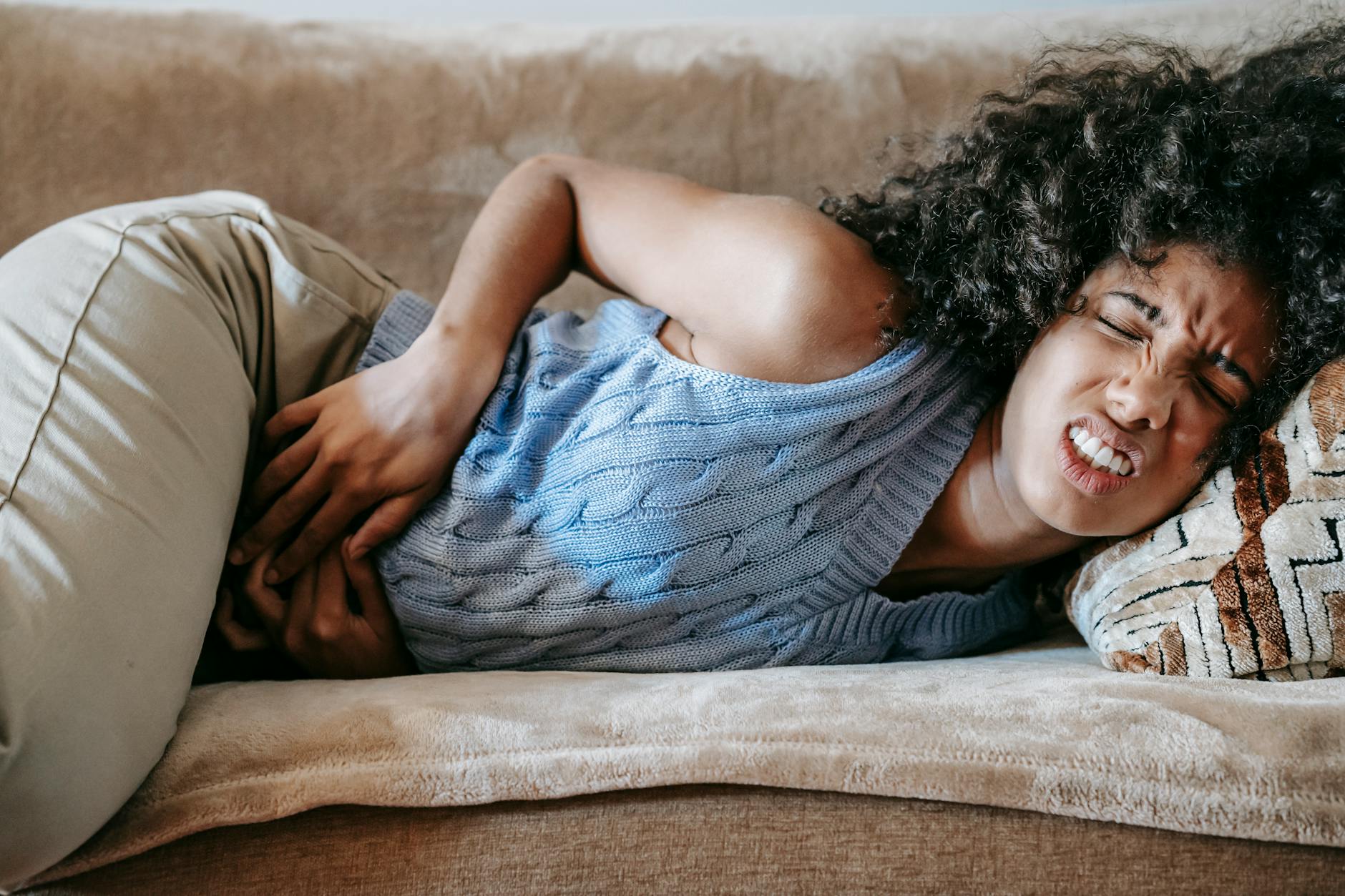
Symptoms of Marburg Virus can appear anywhere from 2 to 21 days after exposure. Early signs include:
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Sore throat
As the disease progresses, more serious symptoms may develop:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Rash
- Severe bleeding from eyes, nose, gums, or internal organs
- Organ failure in critical cases
Prevention
Preventing Marburg Virus relies on careful hygiene and avoiding exposure to infected individuals or animals. Key steps include:
- Avoiding contact with fruit bats and their habitats
- Steering clear of bodily fluids of infected people or animals
- Practicing good hand hygiene and using protective equipment when caring for the sick
- Properly disinfecting surfaces and materials exposed to the virus
- Following safe burial practices for those who die from the disease
What to Do in Serious Conditions
If someone shows severe symptoms of Marburg Virus:
- Seek medical care immediately. Early treatment greatly improves chances of survival.
- Isolate the patient to prevent spreading the virus to others.
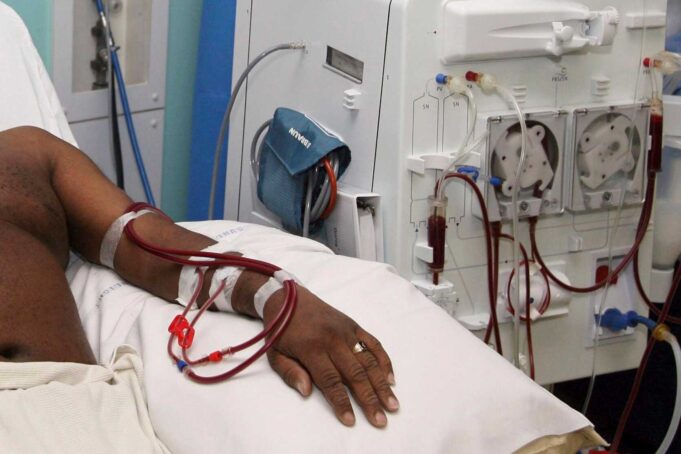
- Supportive care is critical, including hydration, monitoring blood pressure, and treating infections or complications.
- Health professionals may provide antiviral medications or experimental therapies in specialized settings.
Key Points to Remember
- Marburg Virus is rare but extremely serious.
- Transmission occurs through contact with infected bats, animals, or humans.
- Symptoms can start mild but can escalate quickly to severe bleeding and organ failure.
- Early detection, isolation, and supportive care save lives.
- Preventive measures like hygiene, protective gear, and avoiding high-risk areas are crucial.
Understanding the virus and acting quickly can make a critical difference. Awareness, caution, and timely medical attention are the best tools to protect yourself and your community.
Discover more from Hot Stories Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.