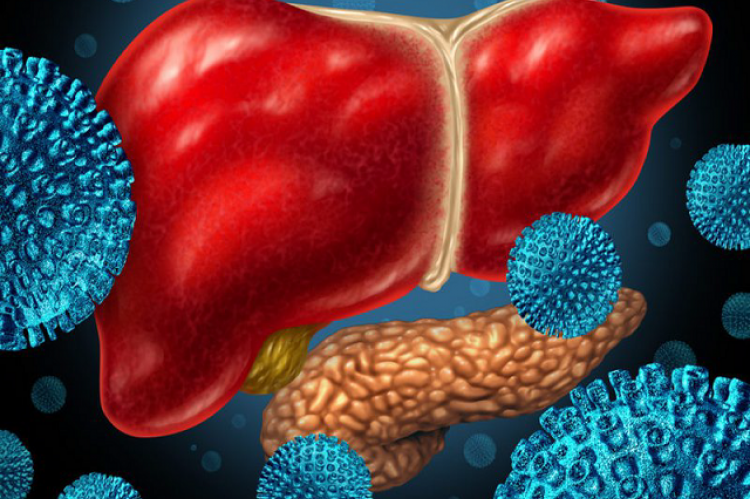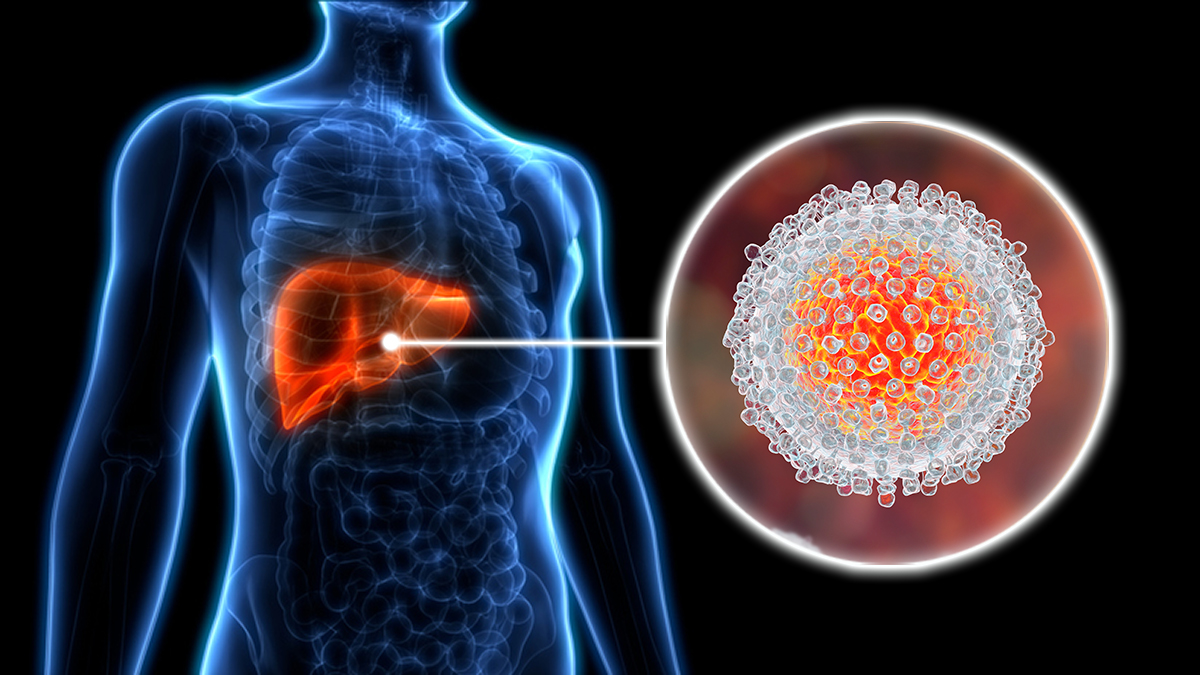
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). Unlike Hepatitis B, there is currently no vaccine for Hepatitis C, making awareness, prevention, and early treatment especially important. The disease can be acute or chronic, with chronic infection potentially leading to severe liver complications, including cirrhosis and liver cancer.
What Causes Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is caused by the Hepatitis C virus, which primarily spreads through blood-to-blood contact. Common transmission routes include:
- Sharing needles or syringes, especially among people who inject drugs.
- Blood transfusions or organ transplants from unscreened donors (rare in countries with strict screening protocols).
- Unsterilized medical or dental equipment.
- Tattooing or body piercing with contaminated instruments.
- Mother-to-child transmission during childbirth (less common).
Hepatitis C is not spread through casual contact such as hugging, kissing, sharing utensils, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is often called a “silent” disease because many people show no symptoms for years. When symptoms do appear, they may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea or poor appetite
- Abdominal discomfort, particularly in the liver area
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Joint pain or muscle aches
Chronic Hepatitis C can eventually lead to:
- Cirrhosis(scarring of the liver)
- Liver failure
- Liver cancer
Early detection is critical, as treatment is most effective before significant liver damage occurs.
Diagnosis of Hepatitis C
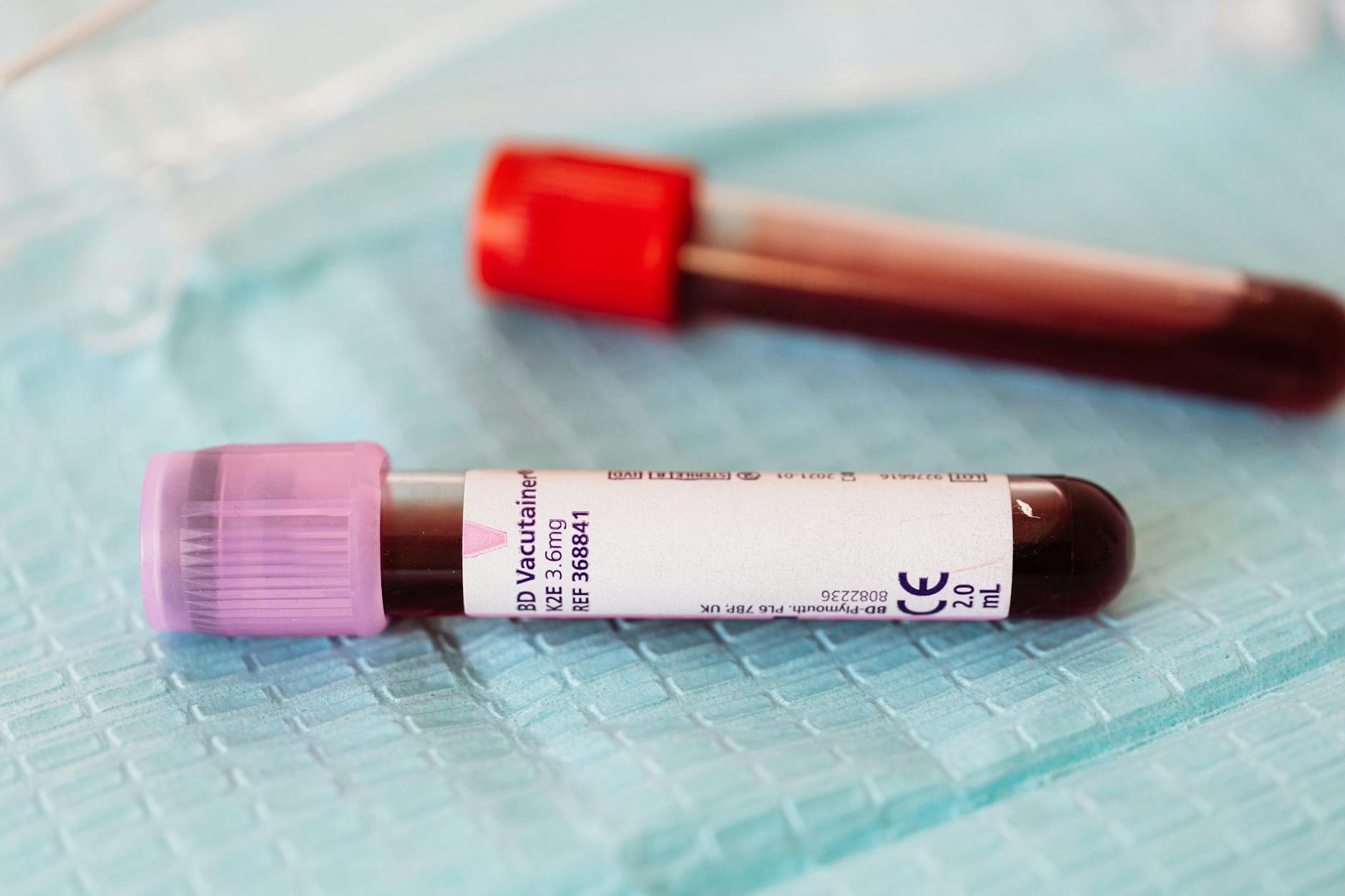
Hepatitis C is diagnosed through blood tests:
- Anti-HCV antibody test:Detects whether a person has ever been exposed to HCV.
- HCV RNA test:Confirms active infection by detecting the virus in the blood.
- Liver function testsand imaging may also be used to assess liver damage.
Prevention of Hepatitis C
There is currently no vaccine for Hepatitis C, so prevention focuses on reducing exposure to infected blood:
- Avoid sharing needles or other injection equipment.
- Ensure medical procedures use sterilized equipment.
- Practice safe tattooing and piercing at licensed facilities.
- Screen blood products before transfusion.
- Use condoms if a partner is infected (though sexual transmission is less common).
- Mother-to-child prevention: Pregnant women with Hepatitis C should discuss treatment and monitoring with their healthcare provider.
Treatment of Hepatitis C
Treatment for Hepatitis C has advanced significantly in recent years, with direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications now able to cure most patients within 8–12 weeks.
- Acute Hepatitis C:Some cases resolve spontaneously, but most require antiviral therapy to prevent chronic infection.
- Chronic Hepatitis C:Treatment includes DAAs that target the virus and prevent liver damage.
Additional management strategies include:
- Regular liver monitoring
- Avoiding alcohol and substances harmful to the liver
- Vaccinations for Hepatitis A and B if the patient is not immune
Successful treatment can prevent long-term complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Living with Hepatitis C
People with Hepatitis C can maintain healthy lives by:
- Following prescribed treatment protocols
- Getting regular medical check-ups to monitor liver health
- Avoiding alcohol and hepatotoxic medications
- Not sharing personal items that may have blood traces (razors, toothbrushes)
- Informing sexual partners and taking precautions
Key Facts to Remember
- Hepatitis C is primarily blood-borne and often silent.
- There is no vaccine, so prevention relies on safe practices.
- Chronic infection can lead to serious liver disease if untreated.
- Modern antiviral treatments can cure most cases effectively.
- Early diagnosis is crucial for preventing long-term complications.
Conclusion
Hepatitis C is a global health challenge due to its silent progression and lack of vaccine. Awareness, routine testing, and early treatment are key to preventing liver damage and improving outcomes. Protecting yourself from exposure to infected blood and seeking medical care promptly are the most effective ways to combat Hepatitis C.
Discover more from Hot Stories Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.