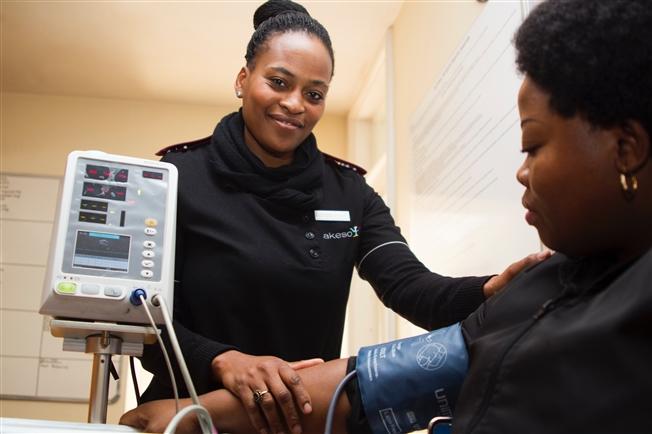
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose), a vital source of energy for the body’s cells. When the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use it effectively, blood sugar levels rise, leading to a variety of health complications over time.
Causes of Diabetes
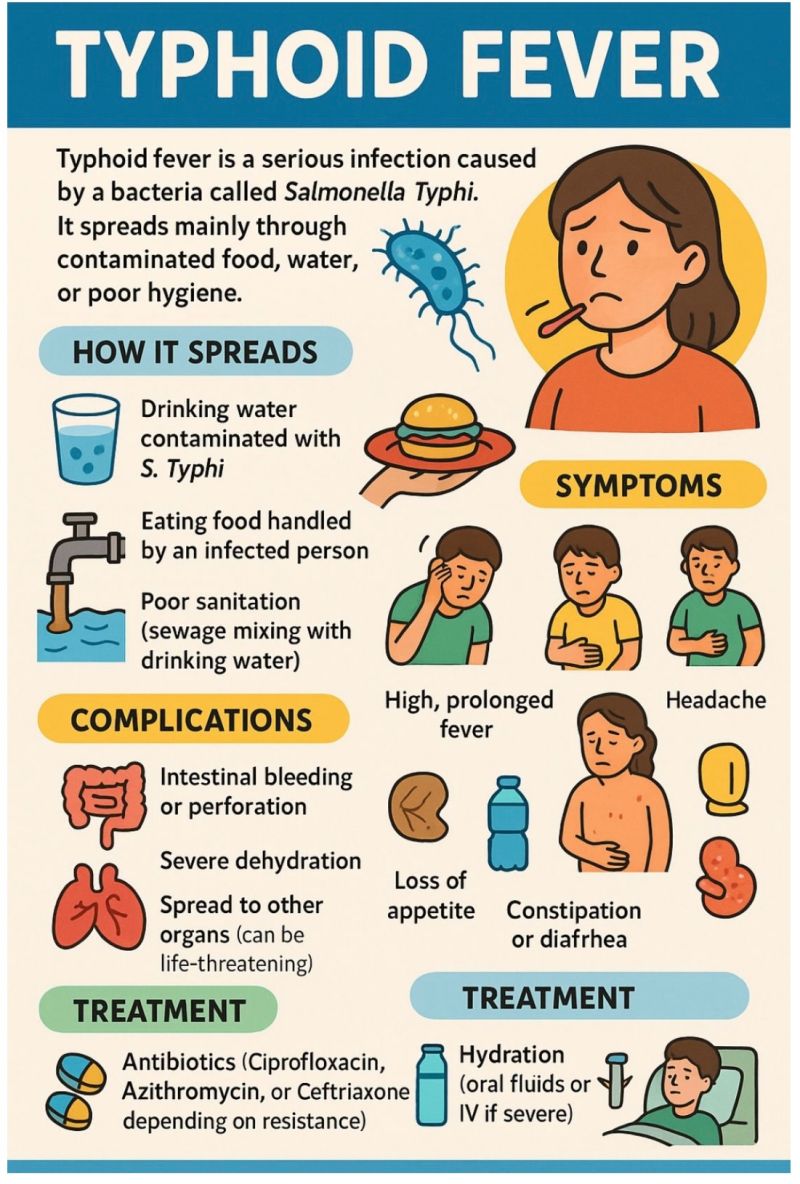
Diabetes is generally classified into Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes, each with different causes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The exact cause is unclear but may involve genetic and environmental factors.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Often linked to obesity, poor diet, lack of exercise, and genetics. In this type, the body either resists insulin or does not produce enough.
- Gestational Diabetes: Develops during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that affect insulin’s effectiveness.
Other risk factors include family history, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and chronic stress.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Common signs include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
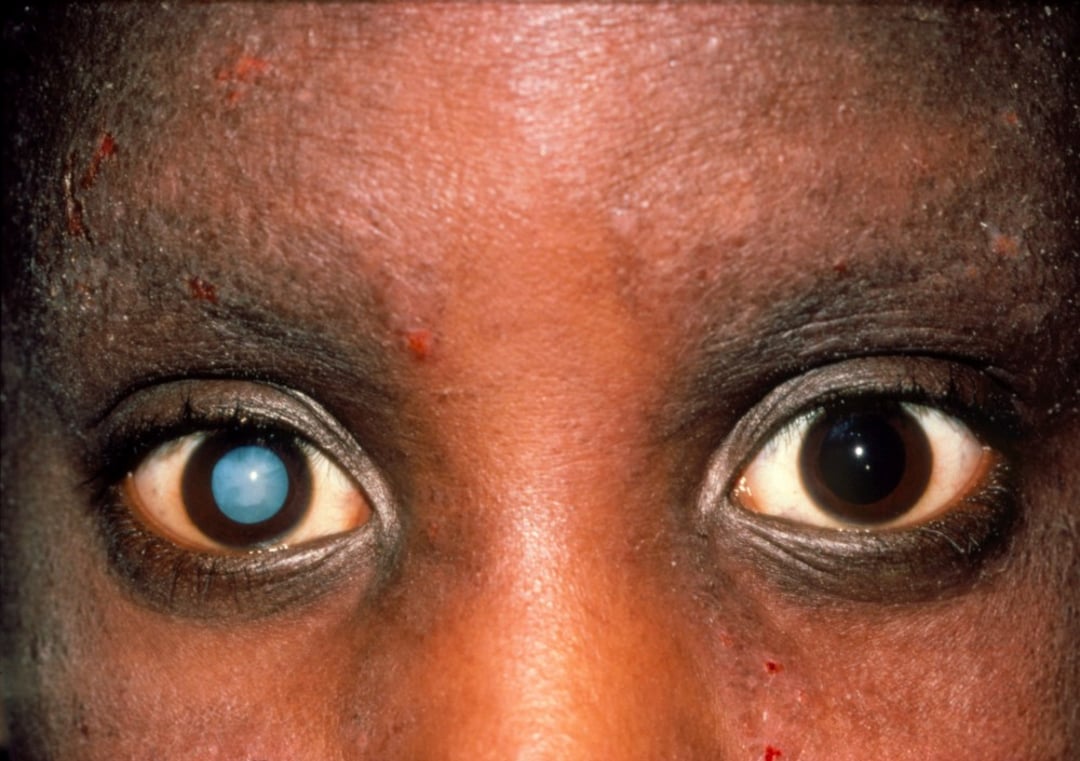
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds or frequent infections
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
Symptoms can appear suddenly in Type 1 diabetes, while Type 2 diabetes may develop gradually and go unnoticed for years.
Prevention of Diabetes
While Type 1 diabetes cannot currently be prevented, Type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes can often be avoided with lifestyle changes:
- Maintain a healthy weight and balanced diet
- Exercise regularly (at least 30 minutes daily)
- Limit sugary foods and drinks
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
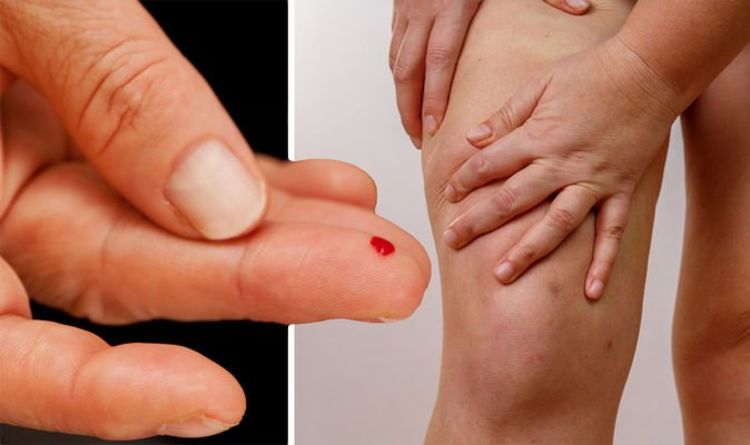
- Monitor blood sugar levels, especially if at risk
Pregnant women should attend regular prenatal check-ups to monitor for gestational diabetes.
Treatment of Diabetes
Treatment focuses on managing blood sugar levels to prevent complications:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Requires daily insulin injections or use of an insulin pump, along with regular blood sugar monitoring.
- Type 2 Diabetes: May start with lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or insulin therapy if necessary.
- Gestational Diabetes: Managed with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and monitoring blood sugar levels; some cases may require insulin.
In all types, regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor complications affecting the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
Living with Diabetes
With proper care, individuals with diabetes can live full, healthy lives. Monitoring diet, staying active, adhering to medication schedules, and attending routine medical check-ups are crucial steps to prevent complications and maintain overall well-being.
Discover more from Hot Stories Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.